What is it?
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Fatty liver (steatosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) is a condition where the liver becomes infiltrated with fat. The fat is called steatosis, but when there is inflammation or scarring, it is called steatohepatitis or NASH.
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Nash, as mentioned above, means there is a presence of hepatic steatosis and inflammation with hepatocyte injury (ballooning) with or without fibrosis. This can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer. Up to 20% of the US population has fatty liver, and perhaps as many as 5% have NASH.
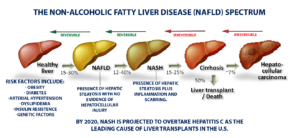
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Spectrum
Who gets it?
How do I know if I have it?
How is it evaluated?
A new ultrasound-based machine called Fibroscan (transient elastography) can diagnose fatty liver and determine the presence of liver scarring. The test is simple, does not expose you to radiation and takes a couple of minutes. If you have risk factors for fatty liver such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, high lipid levels, or significant alcohol consumption; consider getting the Fibroscan test done to assess the health of your liver.
If the results from the Fibroscan show significant scarring then a liver biopsy is still the gold standard to diagnosis steatohepatitis (NASH).
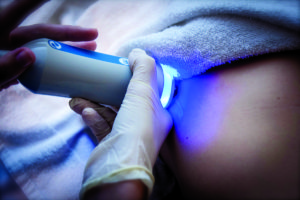
FibroScan is an easy and convenient option to stage liver disease.